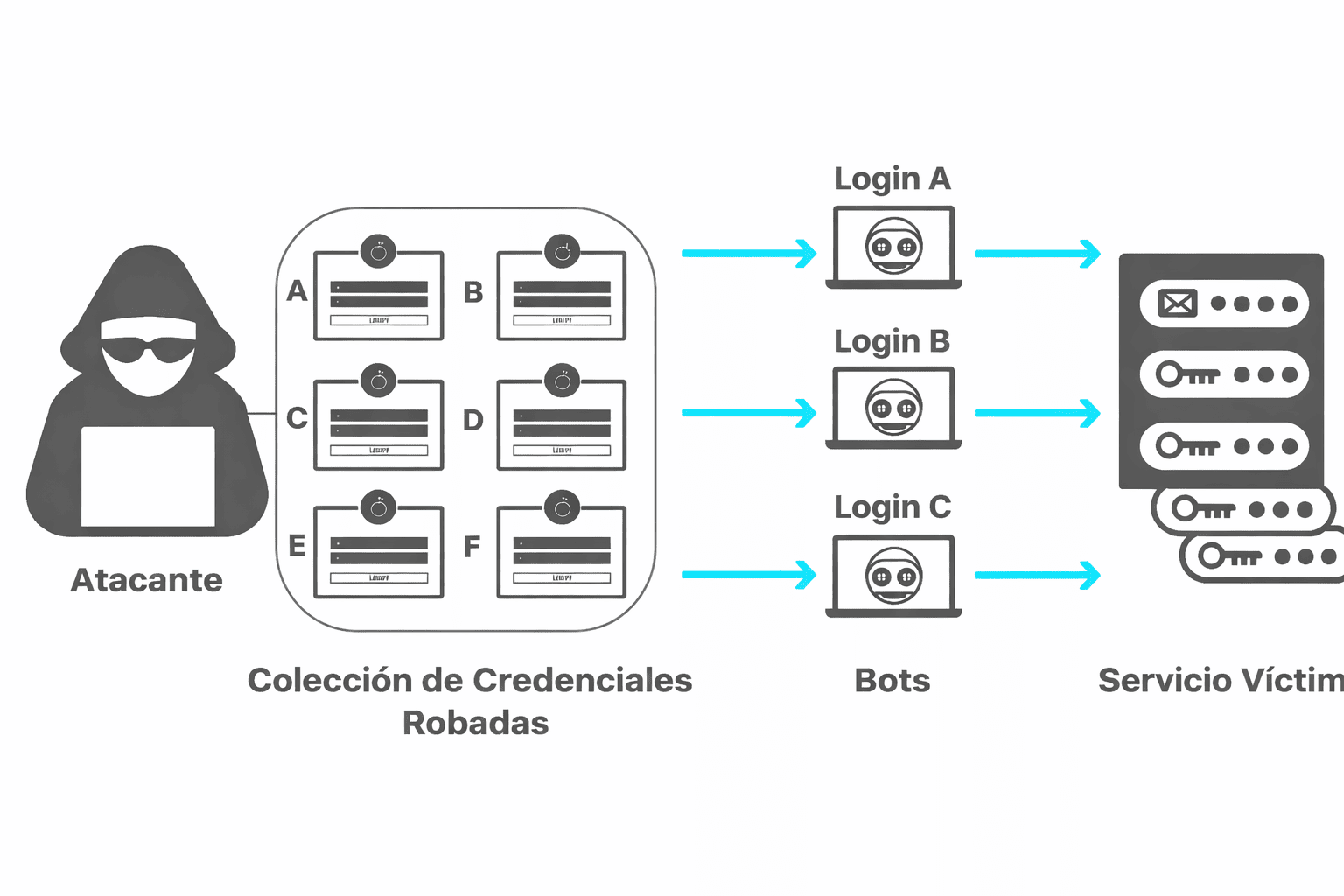
Cybersecurity is a crucial aspect of our digital life. Among the most common threats is phishing, a technique used by cybercriminals to deceive users and obtain personal information, such as access credentials, banking data or confidential information.
Phishing is based on impersonating trusted entities (banks, technology companies, government institutions, etc.) to trick victims into falling into the trap.
How does phishing work? Techniques that cybercriminals use to trick you
Phishing is based on impersonating trusted entities (banks, technology companies, government institutions, etc.) to trick victims into falling into the trap. Here we explain the most commonly used techniques:
- Fake emails: attackers send fraudulent emails that appear to come from a real entity. They include links to fake pages asking for personal data.
- Cloned web pages: Web sites almost identical to the original ones are created for the victim to enter his or her credentials.
- Fraudulent text messages (smishing): Sent via SMS with dangerous links.
- Vishing phone calls: A supposed representative of a company or bank calls asking for confidential information.
- Malvertising: False advertising on the Internet that redirects to fraudulent websites.
- Impersonation on social networks: Fake accounts that impersonate companies or trustworthy people to defraud.
How to identify a Phishing attempt? Warning signs you should not ignore
Phishing attacks can be difficult to detect, especially when they are well designed. However, there are signs that can help you identify a scam attempt before it’s too late.
One of the first things you should check is the sender of the email. If the message comes from an unknown or slightly altered address (e.g., “soporte@banco-seguro.com” instead of “soporte@bancoseguro.com”), this is a clear red flag. Attackers often use minor variations in addresses to fool unsuspecting users.
Another common clue is the wording of the message. Do you notice grammatical errors or poorly structured sentences? Often, cybercriminals are not fluent in the language and their emails are full of spelling mistakes. If you receive a message from your bank with obvious errors, be immediately suspicious.
Urgency is also a recurring strategy. Phrases such as “Your account will be blocked in 24 hours if you do not update your information” seek to generate panic so that you make hasty decisions. If an email or SMS message tries to pressure you into acting without thinking, it’s best to stop and check before clicking on any link.
Speaking of links, here comes another common trick. Before clicking on a suspicious link, hover over it without clicking. This way you will be able to see the actual URL it will take you to. If the link looks strange, too long or does not match the company’s official website, it is best to avoid it.
Finally, unexpected attachments are a huge risk. Receiving a document or compressed file from an unknown sender is reason enough not to open it. Attackers often hide malware in these files to infect your device and steal sensitive information.
If you pay attention to these details, you will significantly reduce the risk of falling for a phishing attack. The key is caution: check, analyze and never act in haste when faced with suspicious messages.
Are you interested in cybersecurity?
Are you interested in cybersecurity?

Types of Phishing: What are the most common forms of attack?
Traditional Phishing
This is the classic method that most people have encountered at some point. Attackers send emails that appear to come from legitimate institutions such as banks, service providers or even popular businesses. These messages usually include links to fake websites designed to capture your credentials or personal data.
Spear Phishing
This is a more sophisticated and personalized attack. Unlike traditional phishing, spear phishing specifically targets specific individuals or companies. Attackers research their victim to personalize the message, making it appear genuine and relevant.
Smishing
Phishing is not limited to email. Smishing uses SMS messages or instant messaging applications to send malicious links or fake phone numbers. Typically, these messages create a sense of urgency, such as warnings of blocked accounts or enticing promotions.
Vishing
Here the attack is carried out via phone calls. Fraudsters pose as employees of banks, technical services or government institutions to obtain confidential information. They often use intimidation tactics or emotional manipulation.
Pharming
This is a more technical attack that manipulates the DNS (Domain Name System) to redirect the user to fake websites without the user noticing. Unlike traditional phishing, it does not rely on the victim clicking on a link, but automatically redirects their traffic to a fraudulent site.
The importance of staying protected in the digital age
Phishing is one of the biggest threats on the Internet. Staying informed, being cautious and applying good digital security practices is key to avoid falling into these traps. Protect your information and help raise awareness about the risks of phishing.
You know what phishing is... now learn how to avoid it
Now that you know what phishing is, how it works and what signs to look out for to detect it, it’s time to take the next step: learning how to protect yourself in a practical and effective way. In our article 👉 How to avoid phishing
Here you will find clear and actionable recommendations to keep your information safe on a daily basis. Because understanding the problem is just the beginning… taking action is what really makes the difference.