In an increasingly connected world, keeping our devices secure has become as important as locking the door at home. Malware poses a real and constant threat. However, the good news is that protecting yourself from malware is within everyone’s reach.
You don’t need to be a tech expert to take control of your digital security. With a few best practices, the right tools and a little attention, you can greatly reduce the risk of an attack. In this article we will show you in a clear and practical way how to shield your device against malware, from choosing a good antivirus to browsing responsibly.
Because when it comes to cybersecurity, prevention is not only the best defense… it’s the smartest.
How to avoid malware?
Want to know how to prevent malware? With good digital security habits, avoiding malware is entirely possible. Here are the keys to keeping your device safe.
Install a reliable antivirus

Antivirus is the first line of defense against malware. Make sure you use a reliable security solution and keep it updated.
Keep software up to date
System and application updates fix vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. Enable automatic updates whenever possible.

Download applications only from trusted sources
Avoid downloading software from unknown websites. Always use official stores such as the Google Play Store or the App Store.

Do not click on suspicious links
System and application updates fix vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. Turn on automatic updates whenever possible.

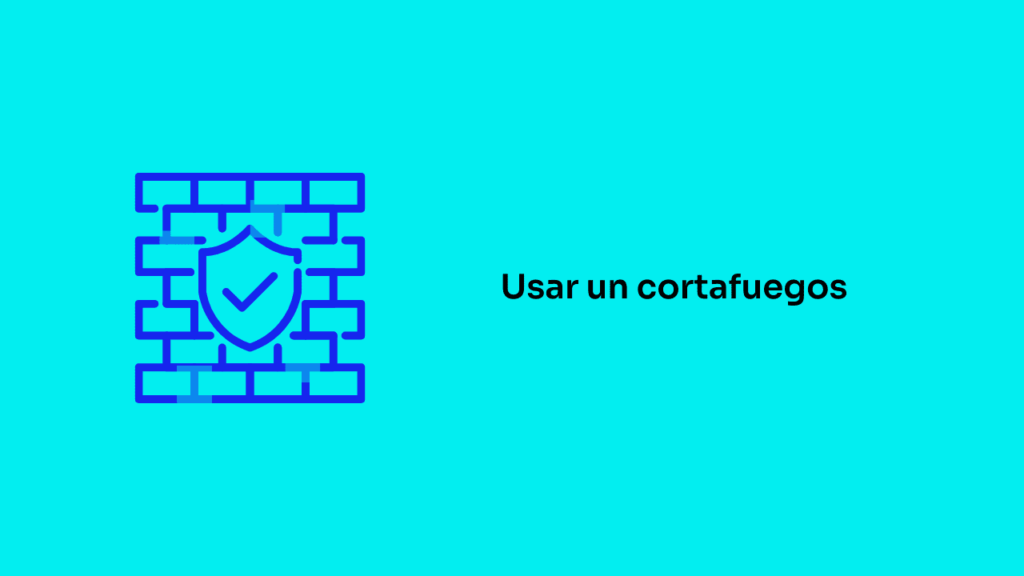
Use a firewall
A firewall acts as a barrier between your device and external threats, blocking unauthorized connections.
Back up
If you suffer a ransomware attack, an updated backup can be your lifesaver. Store your important files in the cloud or on an external drive.

Prevention is power
Malware is a constant threat, but with prevention and good security habits, you can minimize the risks and protect your information.
✅ Know the types of malware and how they act
✅ Install an antivirus and keep your software up to date
✅ Avoid clicking on suspicious links
✅ Make regular backups.
Staying informed is the best weapon against cyber-attacks.
At TRUST Lab we believe that the best defense is knowledge. If you’re interested in staying informed about cybersecurity, privacy and data protection, we have exclusive content that can help you.
Subscribe to our newsletter and receive practical tips directly to your inbox.
Frequently Asked Questions
Some common signs of malware infection include:
- The device is running slower than normal.
- Pop-ups or strange advertisements open.
- Applications close or open on their own.
- Unexpected changes in the browser (home page or search engine).
- Loss of system control or erratic behavior.
- Unknown programs installed without your permission.
👉 The best way to confirm this is to scan your device with an updated antivirus.
Malware can cause multiple consequences, depending on the type:
- Theft of personal data (passwords, cards, identity).
- Remote control of the device without your knowledge (botnets).
- Damage to the system or files (ransomware or Trojans).
- Loss of performance and resources (cryptocurrency mining).
- Spying through camera or microphone.
In short: it can affect both your privacy and the operation of your devices.
Yes, most malware can be removed with appropriate tools.
Basic steps to do so:
- Start your computer in safe mode (to prevent malware from running).
- Use an up-to-date antimalware or antivirus (Malwarebytes, Avast, Bitdefender, etc.).
- Delete temporary files and uninstall suspicious programs.
- Restore the system if necessary.
👉 In severe cases, it may be necessary to format the system or reinstall the operating system.
Malware can attack:
- Operating system files (to corrupt it or spy on it).
- Web browsers (to hijack sessions or inject advertising).
- Banking or email applications (to steal credentials).
- System memory or active processes.
- External devices connected to the computer (USB, hard drives).
You can also attack servers, WiFi networks or even smart cameras and IoT devices.
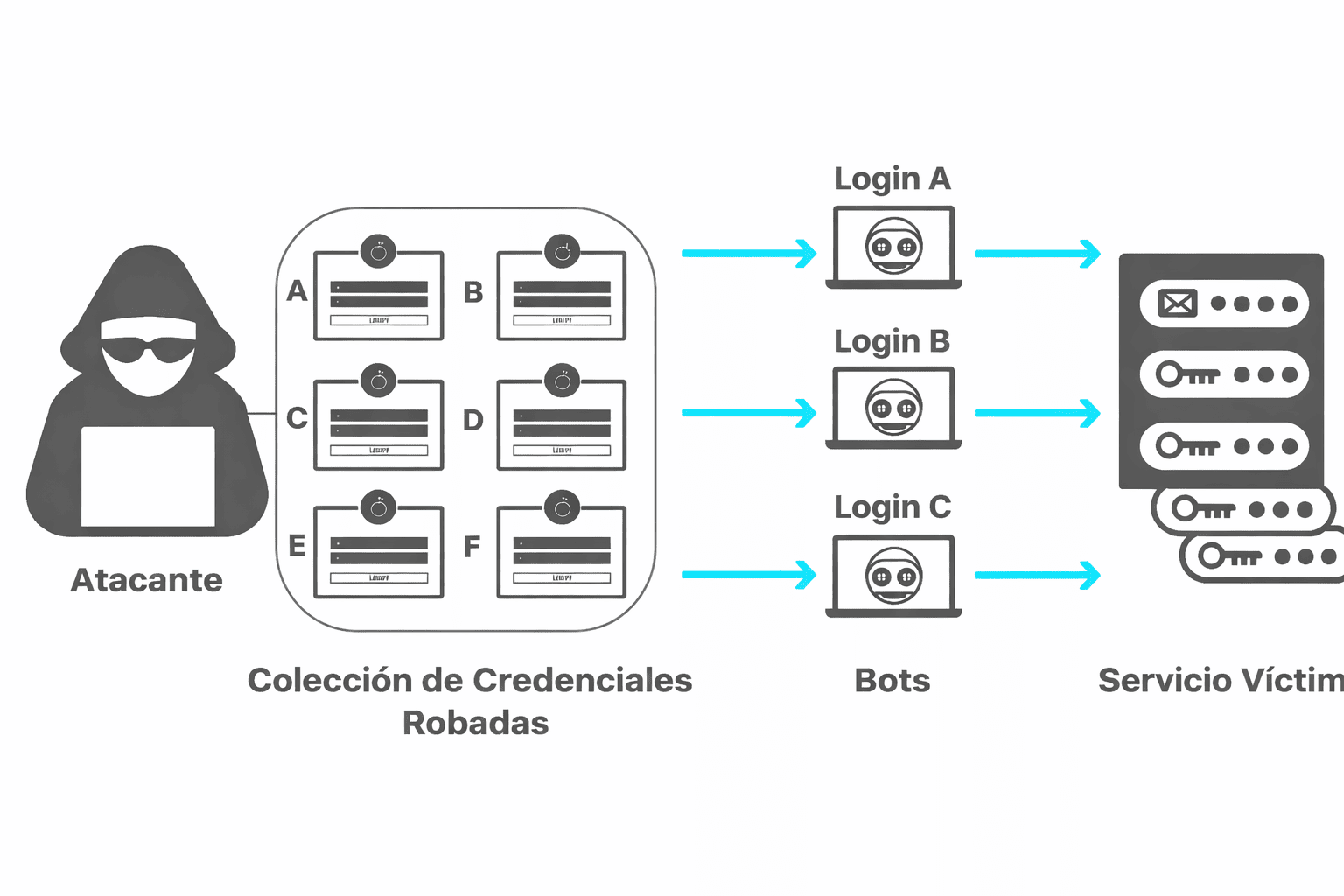
The most common ways of infection include:
- Downloading software or files from dubious sources.
- Clicking on malicious links in emails, social networks or websites.
- Visiting compromised web pages.
- Using infected USB sticks.
- Opening attachments without verifying the sender.
- Installing disreputable browser extensions.
💡 A single click is enough to infect you if you are not protected.